Are you considering dental implants as a solution for missing teeth? You’re not alone! Dental implants have revolutionized oral health, offering a reliable, long-lasting way to restore your smile. In this guide, we will explore the anatomy of dental implants, their components, and how they work together to seamlessly integrate into your mouth, enhancing both function and aesthetics.
Understanding the Components of Dental Implants
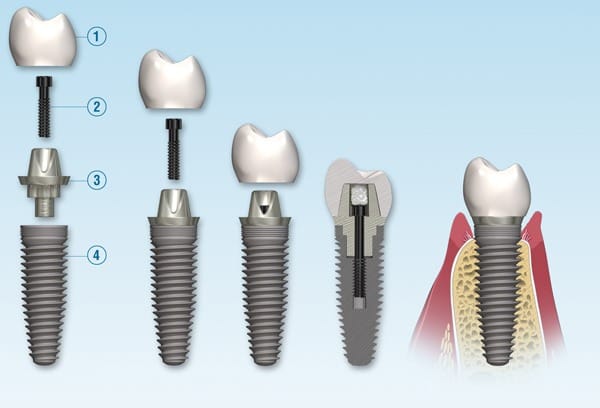
Dental implants consist of three main components, each playing a crucial role in the overall structure and function of the implant.
The Implant Fixture
The implant fixture is the foundation of the dental implant, resembling the root of a natural tooth. Typically made from titanium or zirconia, this component is surgically inserted into the jawbone. Its design often resembles a screw or cylinder, which allows it to anchor securely within the bone.
The Abutment
The abutment serves as a connector between the implant fixture and the visible crown. Made from materials such as titanium, zirconia, or ceramic, the abutment is designed to blend seamlessly with the crown while providing stability. This small but vital piece ensures that the crown remains securely attached to the implant.
The Crown
The crown is the visible portion of the implant that resembles a natural tooth. Crowns can be crafted from various materials—including porcelain, ceramic, or even gold—depending on aesthetic preferences and budget considerations. The crown is custom-made to match the color and shape of your natural teeth, ensuring a cohesive appearance.
How Dental Implants Work Together
When you receive a dental implant, these components work harmoniously to restore your smile:
- The implant fixture is embedded in your jawbone, mimicking a natural tooth root.
- The abutment connects this fixture to the crown, which is visible when you smile or speak.
- Together, they provide stability and functionality, allowing you to eat and speak with confidence.
Benefits of Dental Implants
Dental implants offer numerous advantages over traditional dentures or bridges:
- Bone Preservation: Implants stimulate the jawbone, preventing deterioration that often occurs after tooth loss.
- Improved Functionality: Unlike dentures, which can slip or shift, implants provide a stable foundation for chewing and speaking.
- Natural Appearance: Custom crowns ensure that your new teeth blend seamlessly with your existing ones.
The Implant Placement Process: Step-by-Step
Understanding the process involved in getting dental implants can help demystify their complexity:
- Initial Consultation: Your dentist will evaluate your oral health through X-rays and assessments to determine if you’re a suitable candidate for implants.
- Surgical Placement: During an outpatient procedure, the implant fixture is surgically placed into your jawbone under local anesthesia or sedation.
- Osseointegration: Over several months, your jawbone will fuse with the implant in a process called osseointegration. This step is crucial for long-term stability.
- Abutment Attachment: Once osseointegration is complete, an abutment is attached to the implant fixture through a minor procedure.
- Crown Placement: Finally, your custom-made crown is securely attached to the abutment, completing your restoration.
Maintaining Your Dental Implants
Proper care and maintenance are essential for ensuring the longevity of your dental implants:
- Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing are vital for maintaining gum health around implants.
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine visits to your dentist help monitor implant health and catch any potential issues early.
- Lifestyle Choices: Avoid habits like smoking that can negatively impact oral health and implant success.
Conclusion
Dental implants are an exceptional solution for restoring missing teeth—offering durability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. By understanding their anatomy and benefits, you can make informed decisions about your oral health. If you’re ready to explore how dental implants can transform your smile, consult with a qualified dental professional today!
For more information on dental implants and their benefits, visit reputable sources like American Academy of Implant Dentistry or American Dental Association.
What Are the Three Main Components of a Dental Implant?
Dental implants consist of three primary components: the fixture (or implant post/screw), which is embedded into the jawbone; the abutment, which acts as a connector between the fixture and the prosthetic; and the dental prosthetic itself (such as a crown, bridge, or denture), which serves as the visible and functional tooth replacement.
How Does a Partial Tooth Implant Differ from a Complete Dental Implant?
A partial tooth implant typically refers to an implant that replaces part of a tooth or a single tooth, using a smaller fixture and often a single crown as the prosthetic. In contrast, a complete dental implant may involve replacing an entire tooth or multiple teeth, sometimes requiring a larger fixture and potentially more complex prosthetics like bridges or dentures.
What is the Role of the Fixture in Dental Implants?
The fixture, often a small titanium screw, plays a crucial role in dental implants by acting as an artificial tooth root. It’s implanted into the jawbone and, through osseointegration, fuses with the bone to provide a stable foundation for the rest of the implant structure.
Can You Explain the Importance of the Abutment in Dental Implants?
The abutment is a vital component in dental implants, serving as the connector between the implant post (fixture) and the dental prosthetic. It ensures the stability and proper alignment of the prosthetic, whether it’s a crown, bridge, or denture, with the implant post.
What Are the Different Types of Dental Prosthetics Used in Implants?
Dental prosthetics in implants vary based on the patient’s needs. They include dental crowns, which are ideal for replacing a single tooth, dental bridges, which are perfect for filling in gaps left by several missing teeth, and dentures, which can replace an entire arch of teeth. Each type of prosthetic is designed to restore functionality and aesthetics to the patient’s smile.