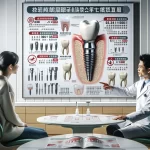
Dental implants have transformed restorative dentistry, offering a long-lasting and natural-feeling solution for individuals with missing teeth . Designed to mimic the function and appearance of natural teeth, these innovative tooth replacements have become a popular and reliable option. This comprehensive guide explores the materials that constitute dental implants, their unique characteristics, and how they contribute to the success of this widely sought-after dental treatment.
Understanding the Structure of Dental Implants
Before diving into the specific materials, it’s essential to understand the fundamental components of a dental implant:
- Implant Fixture: This is the part surgically implanted into the jawbone, serving as an artificial tooth root. It provides the foundation for the entire implant system.
- Abutment: This component acts as a connector, attaching to the implant fixture and extending above the gum line. It serves as the base to which the crown is connected.
- Crown: The visible, tooth-like part that is attached to the abutment, restoring the tooth’s appearance and function. It is custom-designed to blend seamlessly with the surrounding teeth.
Each of these components may be constructed from different materials, carefully selected based on their specific properties and functional requirements.
Key Materials Used in Dental Implants
Titanium: The Industry Standard

Since their introduction in the 1960s, titanium implants have become the gold standard in implant dentistry . This is due to titanium’s exceptional biocompatibility and ability to integrate with bone.
- Biocompatibility: Titanium exhibits excellent compatibility with human tissues, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions or adverse responses .
- Osseointegration: One of titanium’s most remarkable properties is its ability to fuse directly with the surrounding bone tissue, a process known as osseointegration . This creates a strong and stable foundation for the artificial tooth.
- Durability: Titanium implants are renowned for their strength and resistance to fractures, ensuring long-term performance and reliability .
- Corrosion Resistance: Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion within the body’s environment, further contributing to its safety and longevity .
Titanium implants are primarily available in two forms:
- Commercially Pure Titanium (CPTi): Available in grades 1 to 4, with varying oxygen levels that influence their strength .
- Titanium Alloys: The most common alloy is Ti-6Al-4V (grade 5), which contains 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium to enhance strength .
Zirconia: A Metal-Free Alternative

Zirconia (zirconium dioxide) has emerged as a popular and increasingly viable metal-free alternative to titanium in dental implants .
- Metal-Free Composition: Zirconia is a ceramic material, making it an ideal option for individuals with metal sensitivities or those who prefer metal-free dental solutions .
- Aesthetics: The white color of zirconia offers significant aesthetic advantages, particularly in cases where the implant might be visible, such as in patients with thin gum tissue .
- Biocompatibility: Zirconia exhibits excellent biocompatibility, allowing it to integrate well with bone tissue .
- Strength: Zirconia possesses high strength and fracture resistance, although it is generally considered less strong than titanium .
Many zirconia implants feature a one-piece design, which can streamline the implantation procedure but may also limit flexibility in certain clinical scenarios. While zirconia shows great promise, its clinical history is shorter compared to titanium, necessitating ongoing long-term studies to evaluate its long-term performance .
Materials Used for Abutments
The abutment serves as a crucial connector between the implant and the crown. It can be made from several materials, each with its own advantages:
- Titanium: Provides exceptional strength and durability for the abutment .
- Zirconia: Offers excellent aesthetics, particularly when used with front teeth where appearance is a primary concern .
- Gold Alloys: Though less frequently used, gold alloys offer biocompatibility and strength .
Materials Used for Crowns
The crown, or the visible portion of the implant, plays a vital role in both aesthetics and functionality. Common crown materials include :
- Porcelain: Known for its natural appearance, porcelain can be custom-shaded to perfectly match the surrounding teeth .
- Zirconia: Provides a combination of strength and aesthetics for the crown .
- Metal-Ceramic (PFM): Combines a metal substructure with a porcelain overlay, offering a balance of strength and aesthetics .
- Composite Resin: While less common, composite resin is a more affordable option .
Factors Influencing Material Selection
Selecting the most appropriate material for a dental implant involves considering several crucial factors :
- Patient Health and Medical History: Existing allergies or medical conditions can significantly influence material selection .
- Bone Quality and Quantity: The density and volume of available bone can impact the choice of implant material .
- Implant Location: Front teeth typically require materials with superior aesthetics, while back teeth necessitate stronger materials .
- Aesthetic Goals: Patients with high aesthetic expectations may prefer all-ceramic options like zirconia .
- Budget: The cost of different materials can vary, influencing the final decision .
- Dentist’s Expertise: The dentist’s experience and preferences also play a role in material selection.
Innovations in Dental Implant Technology in 2025
The field of implant dentistry is constantly evolving, with ongoing research focused on new materials and technologies to enhance implant performance . Some of the most promising advancements include:
- Surface Modifications: Researchers are developing advanced coatings and textures to improve osseointegration and accelerate healing times .
- Bioactive Materials: Materials that actively promote bone growth and healing are being investigated .
- 3D-Printed Implants: Custom-designed implants created using 3D printing technology offer significant potential for complex cases .
- Smart Implants: Implants with embedded sensors are being developed to monitor healing and detect potential complications early on .
The Dental Implant Procedure: A Step-by-Step Overview
Creating a functional and aesthetically pleasing tooth replacement involves a series of carefully executed steps:
- Material Processing: The selected material is precisely shaped into the implant using advanced CAD/CAM (computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing) technology.
- Surface Treatment: The implant surface may undergo specialized treatments to enhance osseointegration.
- Sterilization and Packaging: Implants are meticulously sterilized and packaged to maintain their sterility until implantation.
- Surgical Placement: The implant is surgically placed into the jawbone by a qualified dental professional .
- Healing Period: A period of several months is required for the implant to fully integrate with the surrounding bone.
- Abutment Attachment: After successful osseointegration, an abutment is connected to the implant.
- Crown Fabrication and Placement: A custom-designed crown is fabricated and attached to the abutment, completing the restoration process.
Maintaining Your Dental Implants for Long-Term Success
The longevity of dental implants depends on the materials used and, most importantly, on meticulous maintenance and care . To ensure the long-term success of your dental implants:
- Practice Excellent Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings are essential to prevent peri-implantitis and other issues that can lead to implant failure.
- Attend Regular Check-Ups: Routine dental visits allow for the early detection and management of potential problems.
- Avoid Harmful Habits: Smoking, teeth grinding (bruxism), and biting on hard objects can negatively impact implant success.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Overall health and well-being contribute to the long-term success of dental implants.
The Future of Dental Implant Materials
As implant technology continues to advance, significant improvements in materials and techniques are expected, with future implants offering enhanced biocompatibility, accelerated healing, and superior aesthetics . Both titanium and zirconia implants are excellent options for tooth replacement, boasting high success rates . The ultimate decision should be based on individual needs and clinical considerations. Successful dental implants rely on the expertise of skilled professionals, meticulous planning, and the patient’s unwavering commitment to oral health . A thorough consultation with a qualified dental professional is crucial to determine the most suitable material, taking into account factors such as allergies, medical history, and aesthetic preferences .
Zirconia vs Titanium Dental Implants: A Detailed Comparison
To help you make a more informed decision, here’s a detailed comparison of Zirconia and Titanium dental implants:
| Feature | Titanium | Zirconia | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Biocompatible metal | Ceramic material (Zirconium Dioxide) | Titanium is known for its durability and flexibility, while Zirconia is valued for its biocompatibility and aesthetic qualities . |
| Color | Metallic silver; may show through thin gums | White; blends naturally with teeth | Zirconia’s tooth-like color provides a more natural look, especially important in visible areas . |
| Strength | High; suitable for high-stress areas | Moderate to High; better suited for front teeth and low-stress areas | Titanium is exceptionally strong, making it ideal for molars, while Zirconia is strong enough for most front teeth applications . |
| Biocompatibility | High; rarely causes allergic reactions | Very High; ideal for patients with metal sensitivities | Both materials are biocompatible, but Zirconia is often preferred for patients with metal allergies or sensitivities . |
| Durability | Exceptional; lasts many years with proper care | High; also durable but requires careful handling during placement | Titanium implants have a proven track record of lasting many years. Zirconia is also durable but requires precise placement to avoid stress fractures . |
| Flexibility | More flexible; absorbs biting forces well | Less flexible; more rigid | Titanium’s flexibility can help it withstand biting forces, reducing fracture risk. Zirconia’s rigidity can be a benefit in certain applications but requires careful load management. |
| Osseointegration | Excellent; well-documented success | Predictable; may benefit from surface modifications | Both materials exhibit good osseointegration, but titanium has a longer history of successful clinical use . |
| Aesthetics | Metallic color can be a concern in thin gums | Excellent; natural tooth-like appearance | Zirconia offers superior aesthetics, particularly important for front teeth . |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Exceptional | Zirconia is highly resistant to corrosion, ensuring long-term stability in the oral environment . |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Generally more expensive | The cost can vary based on location, dentist, and specific implant needs . |
| Clinical Success | Extensive clinical history | Growing body of evidence | Titanium has a longer clinical history, while Zirconia is gaining popularity with promising results . |
Recent Advances in Dental Implant Technology
The field of dental implants is continuously evolving. Here’s a look at some of the latest advancements:
3D Printing for Customized Implants: 3D printing technology allows for the creation of highly precise implants tailored to each patient’s unique anatomy . This results in faster production times and more affordable implants without sacrificing quality.
Smart Dental Implants: Integrating sensors into dental implants enables real-time monitoring of the implant’s health and surrounding tissues . These implants can detect early signs of infection or failure, providing patients with immediate data about their oral health and enhancing the implant’s lifespan.
Computer-Guided Implant Surgery: Advanced imaging and software allow dentists to plan every aspect of the implant procedure, ensuring optimal placement, improving functionality, and enhancing patient safety . This technology minimizes risks and reduces recovery time.
Enhanced Materials:
- Zirconia Implants: These metal-free implants are ideal for patients with metal allergies and provide excellent aesthetics.
- Enhanced Titanium: Advanced coatings on titanium implants promote faster osseointegration and greater stability.
- Nanotechnology: Nano-textured surfaces encourage better integration with bone, ensuring a secure fit .
Regenerative Solutions: Stem cell therapy is paving the way for more effective dental implant procedures. Stem cells can repair and regenerate bone tissue, making implants possible for patients with severe bone loss and accelerating the healing process.
Minimally Invasive Techniques:
- Flapless Implant Surgery: Placing the implant without making a large incision results in faster healing times and reduced postoperative discomfort.
- Piezosurgery: Using ultrasonic vibrations to cut bone with high precision minimizes damage to soft tissues, preserving soft tissues, reducing bleeding, and promoting faster healing.
AI-Powered Planning: AI algorithms analyze patient data and imaging to guide implant placement, predict potential complications, and determine each patient’s ideal implant size and shape, leading to more natural-looking and longer-lasting results.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Robotic systems enhance precision and efficiency by carrying out implant placement with millimeter accuracy, minimizing the risk of human error and providing real-time data and guidance .
Sustainability: There is an increasing focus on eco-friendly implant materials and sustainable manufacturing practices. Researchers are exploring bioresorbable implants made from materials that naturally integrate with the bone and eventually dissolve, eliminating the need for removal.
Complications and Considerations
While dental implants boast high success rates, potential complications can arise. Understanding these risks is crucial for informed decision-making and proactive management:
- Infection: Infections at the implant site, known as peri-implantitis, can lead to bone loss and implant failure. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene and attending regular check-ups are essential for prevention.
- Nerve Damage: Improper implant placement can potentially damage nearby nerves, resulting in pain, numbness, or tingling in the gums, lips, or chin.
- Sinus Issues: Implants placed in the upper jaw may protrude into the sinus cavity, leading to sinus problems.
- Implant Fracture: Although rare, implant fractures can occur due to excessive biting forces or material fatigue.
- Poor Osseointegration: In some cases, the implant may not properly fuse with the bone, leading to instability and failure.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare with titanium and zirconia, allergic reactions to implant materials can occur in sensitive individuals.
Key Takeaways
Dental implants have revolutionized the field of restorative dentistry, offering a reliable and long-lasting solution for missing teeth. Whether you opt for titanium or zirconia, the choice of material should be based on a comprehensive evaluation of your individual needs, medical history, and aesthetic goals. By staying informed about the latest advancements in dental implant technology and working closely with a skilled dental professional, you can achieve a healthy, functional, and beautiful smile that lasts a lifetime.
What are the main advantages of titanium dental implants?
Titanium implants are known for their durability, biocompatibility, and successful osseointegration with the jawbone, making them a long-lasting solution for tooth replacement.
Can people with metal allergies use dental implants?
Yes, for individuals with metal allergies, zirconia or ceramic implants can be a suitable alternative, as they are hypoallergenic and offer comparable biocompatibility.
How do zirconia implants compare to titanium in terms of aesthetics?
Zirconia implants are preferred for their tooth-like color, making them a more aesthetic choice, especially for front teeth replacements.
What should I consider when choosing the material for my dental implant?
Consider factors like biocompatibility, aesthetics, your medical history (including allergies), and the implant’s longevity. Consulting with a dental professional is crucial in making an informed decision.
How long do titanium dental implants last?
With proper care and maintenance, titanium dental implants can last for several decades, often outliving the patient’s lifespan.