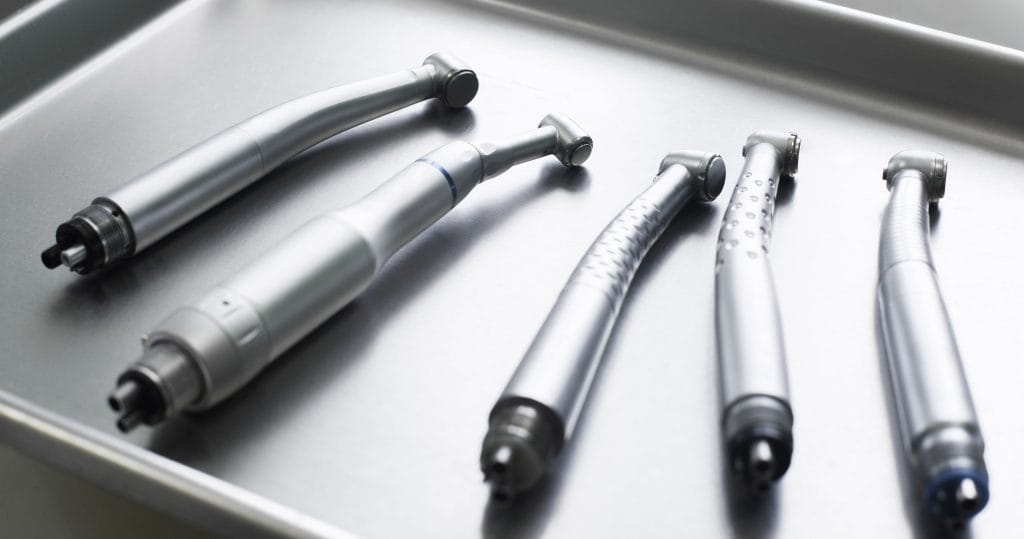
In modern dentistry, dental handpieces are vital instruments that facilitate a range of procedures, from routine cleanings to intricate restorations. With advancements in technology, choosing between electric dental handpieces and air-driven handpieces has become increasingly significant for dental professionals. Each type offers unique benefits and drawbacks that can impact performance and patient outcomes. By understanding these key differences, you can make an informed decision tailored to your practice’s specific needs and preferences.
Power Source: Electricity vs. Compressed Air
The primary distinction between electric and air-driven handpieces is their power source. Electric handpieces utilize an electric motor that converts electrical energy into rotational motion. These devices require either a direct electrical connection or a rechargeable battery pack for operation. In contrast, air-driven handpieces depend on compressed air to spin a turbine, thus generating the necessary rotational force at speeds that can reach up to 400,000 RPM.
This high speed allows them to effectively cut through hard materials but may lack the torque consistency offered by electric models. Additionally, electric handpieces are known for their quieter operation and reduced vibration, which enhances patient comfort during procedures. This compressed air is generally supplied by an in-office compressor system, ensuring consistent performance while also contributing to a noisier environment than that created by electric handpieces.
Speed and Torque: Precision vs. Power
A key distinction between electric and air-driven handpieces lies in their speed and torque capabilities. Air-driven handpieces are celebrated for their impressive speeds, often reaching up to 400,000 revolutions per minute (RPM). This remarkable speed is advantageous for procedures requiring rapid material removal, such as cavity preparations or tooth extractions. However, this high speed comes with a trade-off: lower torque (typically around 20 watts), which can lead to stalling or reduced performance when faced with resistance from harder materials like crowns or bridges.
Conversely, electric handpieces generally operate at lower speeds—between 100,000 and 200,000 RPM—yet they provide significantly higher torque (often exceeding 60 watts). This unique combination allows for more precise cutting and consistent performance under pressure, making electric handpieces particularly suited for delicate procedures such as crown preparations or root canal treatments, where precision is paramount. Additionally, electric handpieces tend to produce less noise during operation compared to their air-driven counterparts, contributing to a more comfortable experience for both dentists and patients.
Noise and Vibration: Patient Comfort Matters
One of the most significant differences between air-driven and electric handpieces is their noise and vibration levels. Air-driven handpieces are often characterized by a high-pitched whine and noticeable vibrations, which can be particularly unsettling for patients, especially those experiencing dental anxiety or sensory sensitivities. Studies show that air-driven handpieces can produce noise levels ranging from 70 dB to over 90 dB, which may exacerbate anxiety in sensitive patients.

In contrast, electric handpieces function with a quieter, lower-pitched hum—typically around 60 dB—and produce significantly less vibration. This smoother operation not only enhances patient comfort, creating a more relaxed atmosphere during procedures but also minimizes the risk of hand fatigue for dentists, enabling them to perform more precise and controlled movements during lengthy procedures.
Maintenance and Longevity: Keeping Your Tools in Top Shape
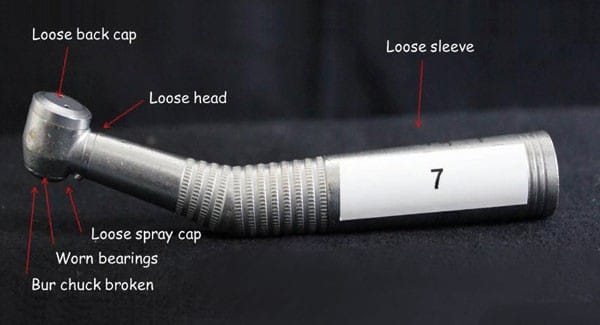
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of dental tools, particularly air-driven and electric handpieces. Neglecting these practices can lead to equipment failure and compromise patient safety. While both types require care, their maintenance needs differ significantly.
Air-driven handpieces: These tools demand frequent attention due to their intricate turbine components. Regular lubrication—ideally after each use—and thorough cleaning are vital to prevent wear and tear, ensuring smooth operation and extending their lifespan. Using ultrasonic cleaners can effectively remove debris from hard-to-reach areas, while autoclaving ensures proper sterilization between patients.
Electric handpieces: Known for their durability, these devices still require periodic upkeep. Tasks such as replacing worn bearings or brushes and lubricating moving parts are necessary to maintain performance. However, their complex electrical components may occasionally necessitate specialized repairs or replacements. Regular inspections for signs of wear can prevent costly repairs down the line.
By adhering to tailored maintenance routines recommended by manufacturers, dental professionals can maximize the efficiency and lifespan of their equipment while enhancing patient care.
Cost Considerations: Balancing Investment and Value
When evaluating costs, air-driven handpieces typically require a lower initial investment than their electric counterparts. However, the cumulative expenses of maintenance and repairs over time may diminish these initial savings. In contrast, electric handpieces, though more expensive upfront, often provide a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs due to their superior torque and consistent performance.

This makes them a potentially more cost-effective option for high-traffic dental practices seeking durability and efficiency. Additionally, electric handpieces offer lower noise levels during operation, contributing to a more comfortable experience for both dentists and patients. Ultimately, the choice between these handpieces should consider not only initial costs but also long-term operational efficiency and specific procedural needs.
Choosing the Right Handpiece for Your Practice
When selecting a dental handpiece for your practice, understanding the key differences between electric and air-driven options is crucial. For routine procedures such as cleanings, fillings, or simple extractions, air-driven handpieces can be an excellent choice due to their high speeds and affordability. Conversely, if your focus is on complex restorative work—like crown preparations, implant surgeries, or endodontic treatments—electric handpieces offer superior precision, control, and higher torque, essential for these delicate tasks.
Moreover, consider additional factors such as patient comfort, ergonomics, and your practice’s overall workflow:
Ergonomics: A comfortable grip and lightweight design help reduce operator fatigue during extended procedures.
Noise Level: Electric handpieces are generally quieter than air-driven models, contributing to a more relaxing environment for patients.
Maintenance and Sterilization: Choose handpieces that are easy to clean and sterilize to ensure longevity.
Electric handpieces are often favored in environments aiming for a quieter atmosphere for patients. In contrast, air-driven handpieces might be better suited for practices prioritizing speed and cost-effectiveness.
Embracing the Future: Advancements in Dental Handpiece Technology
As dental technology evolves, significant advancements are anticipated in both electric and air-driven handpieces. Manufacturers are dedicated to enhancing performance, ergonomics, and efficiency, while also addressing critical issues such as noise reduction and infection control, which are vital for improving patient comfort during procedures.

A notable development is the integration of advanced features like LED lighting, which significantly enhances visibility and improves the accuracy of dental procedures. Furthermore, incorporating digital controls and programmable settings empowers dentists to customize their handpiece’s performance according to specific needs and preferences. Recent innovations include improved turbine designs that offer smoother cutting action and integrated cooling systems that help maintain optimal temperatures during procedures, reducing discomfort for patients.
| Feature | Electric Handpieces | Air-Driven Handpieces |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Electric motor | Compressed air |
| Speed Range | 100,000 – 200,000 RPM | 300,000 – 400,000 RPM |
| Torque | Higher torque (60+ watts) | Lower torque (20 watts) |
| Noise Level | Quieter operation | Louder whirring noise |
| Vibration | Less vibration | More vibration |
| Cutting Action | Smooth, precise cuts | Can stall on harder materials |
| Head Size | Slightly larger heads | Smaller, more compact heads |
| Weight | Heavier handpieces | Lighter weight |
| Maintenance | More complex maintenance | Simpler maintenance |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower initial cost |
| Typical Uses | Crown preps, root canals | Cavity preps, tooth extraction |
| Patient Comfort | Reduced noise/vibration | Noisier with more vibration |
These advancements not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute significantly to a more comfortable experience for both dentists and patients alike, ultimately leading to better treatment outcomes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
In the world of dental handpieces, the choice between electric and air-driven models is not a matter of one being inherently better than the other. Rather, it’s about understanding the unique strengths and limitations of each type and selecting the tool that best aligns with your practice’s needs, your patients’ comfort, and your personal preferences as a dental professional.
Whether you opt for the high-speed precision of air-driven handpieces or the controlled power of electric models, the key is to invest in quality instruments from reputable manufacturers and to maintain them meticulously. By doing so, you can ensure that every procedure is performed with the utmost efficiency, accuracy, and patient comfort, ultimately delivering the highest standard of care.
So, the next time you find yourself in the dentist’s chair, take a moment to appreciate the technology behind those whirring instruments – they may be small, but they play a crucial role in preserving your oral health and providing you with a comfortable, stress-free dental experience.